Prototyping Made Simple: How PCB Board Makers Bring Circuit Board Prototypes to Life
Get Your PCB Quote!
Table of Contents
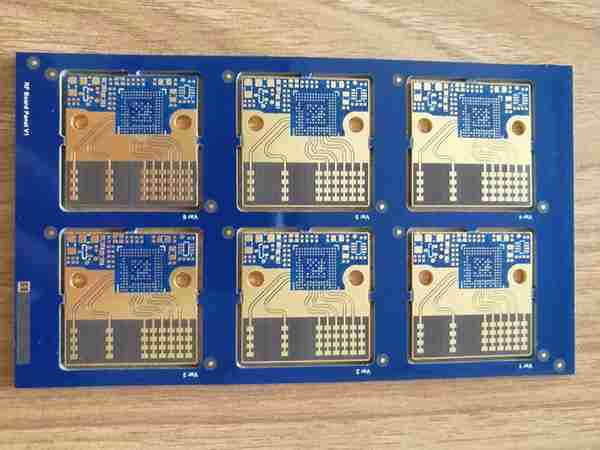
Prototyping as an entity takes on greater significance in developing the electronics so that designers and engineers can test out their ideas and pinpoint problems or hurdles that need to be addressed before going into mass production. An extra vital part of prototyping is the designing of a printed circuit board (PCB) around which electronic components will be assembled. PCB makers are meanwhile crucial in this ecosystem of turning designs into tangible prototypes for testing and refinement.
This article peeks into how PCB designers bring prototypes into life, an overview of the PCB prototyping stages, and the importance of accuracy to arrive at functional prototypes.
The Importance of Prototyping in Electronics Development
Whether it is a consumer device or heavy-duty equipment, every product begins with the prototype. Prototyping allows designers and engineers to verify ideas and fix any potential issues before the next stage of the product entails mass production.
Generally, the prototypes are rough drafts of the final product, pointing to design flaws, functional insufficiencies, and other areas needing fine-tuning. It should be clearly understood that the circuit, in the case of PCB prototyping, must be validated before the manufacturing process.
What is PCB Prototyping?
PCB prototyping involves the production of a sample circuit board according to the design. The actual designing of the PCB layout and functions is normally done by highly specialized design software. This design will detail component positioning, electrical trace routing, and via locations (holes that allow for electrical connection). When all aspects of the design are completed, the PCB contractor builds the prototype.
This prototype permits engineers to validate various parameters on the board, from electrical parametric to signal integrity and performance. With a PCB prototype in hand, they can ascertain that the design meets all the criteria expected of it, which is actually a time-saving and money-saving practice indeed.
The Role of PCB Board Makers in Prototyping
PCB board makers are the specialists who manufacture circuit board prototypes based on engineers’ designs. They turn digital designs into real prototypes with high precision and an eye for details. The process of PCB prototyping consists of several stages where each stage requires particular expertise.
Design Verification and File Preparation
The first step in the process involves verifying the design files. Engineers give the PCB board maker the design by means of files (usually Gerber files) that detail the exact layout of the circuit board. These will involve the copper layers, vias, components, and all other quite important elements.
The PCB maker will then check the files with respect to error. If faults are detected, they may work with the design team to get it corrected before going ahead with the fabrication.
Materials Selection
The different selection of materials used for PCBs considerably influences the functional performance and life of such boards. Different types of boards can be manufactured from several materials, ranging from fiberglass to polyimide, etc. On the other hand, the materials would be selected based upon what the PCB prototype was intended for.
Thus, for instance, a board may require certain materials that can withstand higher frequencies associated with high-speed applications without degrading the signal. In contrast, boards meant to be operated in harsh environments may be coated with special types of coatings so that moisture, heat, or chemicals do not reach the circuit.
PCB Fabrication
The fabrication process commences with the acquisition of the design and materials. The procedure consists of various steps:
1. Printing the Design onto the PCB: The design is transferred onto the board via the photolithographic procedure. In this, a light-sensitive layer is applied onto the surface of the PCB, which is then exposed to UV light, allowing a pattern to develop matching the design.
2. Etching the Board: After printing, the excess copper is bulldozed away through chemical etching, leaving behind copper traces that comprise the electrical connections on the board.
3. Drilling: The PCB is drilled for holes, which accommodate components, vias, and mounting holes. This step is concerned with accuracy, since the position and size of the holes have to be exact.
4. Plating: Copper is carefully added to the drilled holes to provide electrical interconnection between the layers of the PCB. This becomes critical for multilayer PCBs, where signal traces may need to connect between different layers.
5. Solder Masking and Silkscreen: The solder mask is applied over the board to protect the traces and to avoid solder from bridging the connections during assembly. The silkscreen layer is printed to label the components and provide other necessary markings.
Assembling the PCB Prototype
The next stage of PCB fabrication involves component assembly by placing components on the board, which include resistors, capacitors, microchips, and connectors. Two primary methods of component assembly include:
• Through-Hole Technology (THT): This process involves the insertion of component leads into PCB holes for soldering on the other side. This technique is chosen when there is the need for strong mechanical bond with the component.
• Surface-Mount Technology (SMT): It allows for mounting directly onto the PCB, with soldering done in place. SMT enjoys speed, thus cost-effective for mass production.
The choice of assembly method is dependent on the component in use and the strength desired from the board.
Why Precision Matters in PCB Prototyping
Precision Control becomes critical for PCB prototype fabrication. Not even the smallest error in design or fabrication may lead to fatal performance impacts or complete failure of a board. This is the reason that PCB board makers invest in the latest technology equipment as well as stringently control the quality through every step of production.
In Conclusion
PCB makers play an essential role in prototyping for the development of working and high-quality electronic devices. Creating accurate circuit board prototypes allows design engineers to test their designs, troubleshoot problems, and optimize performance. The prototyping process allows for rapid test and iteration, giving developers the flexibility to tweak their designs before mass production begins. Such an approach mitigates the risk of incurring massive losses and delays while guaranteeing that the final product is working and reliable.
Table of Contents
Get Your PCB Quote!