Printed Circuit Board Assembly: Key Steps and Best Practices
Get Your PCB Quote!
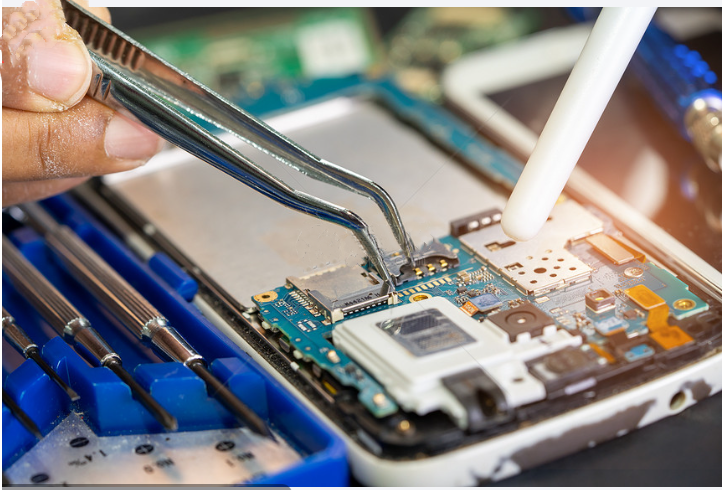
Printed Circuit Board Assembly is much more than processes of putting a bare board forming up into functioning devices. Understanding the essential steps of PC board assembly and practices of PC board assembly ensure reliability and performance in electronic products:
1. Design for Manufacture Reviews
The final step before commencing PCB assembly is conducting a thorough DFM review. This will require assessing the PCB design concerning manufacturing capabilities and standards. It minimizes costly revisions and delays as potential issues are caught early through a delightfully meticulous DFM review.
2. Solder Paste
The assembly begins with solder paste application to the PCB pads. This is normally done with a stencil to ensure accurate deposition of paste. Solder paste application is critical for holding components in preparation for their subsequent soldering process.
3. Component Placement
Component placement onto the PCB after the application of solder paste follows the use of automated pick and place machines to prep, position surface-mounted through-hole components at high levels of precision by coordinates alignment and orientation.
4. Soldering
Soldering comes next after component placement. There are two major processes used in PCB assembly:
Reflow Soldering: Mostly for surface-mounted devices, where the board passes through a reflow oven that melts and fuses the solder paste to set up electrical connections.
Wave Soldering: This is mainly to insert through-hole devices, with the board passing through a wave of molten solder to establish the connection.
Both approaches require stringent temperature control in order to avoid defects and to ensure strong solder joints.
5. Inspection and Quality Control
All assembled circuits will be subjected to a rigorous inspection for defects and alignment misalignments. Thereby all joints of solder and positions of components are secured by automated optical inspection and x-ray inspection.
6. Testing
Functional testing helps check whether the assembled PCBA circuit board is working according to expectations. This may include in-circuit testing of all the components together with full system testing.
7. Cleaning
After running tests on a board, they are washed of flux and other impurities. Depending on the soldering process, cleaning may include solvents or deionized water to ensure boards have cleanliness standards.
8. Final Inspection and Packaging
The final inspection confirms that the PCBs meet all quality and performance criteria just before packaging; the approved board is packaged to minimize chances of damage during transportation and storage.
Importance of Prototype in PCB Assembly
Prototypes are crucial in the assembly of printed circuit boards as they help find design defects before mass production. A prototype stands the chance of being a well-rounded one that can make engineers test functionality, assess component placement, and refine the design towards better performance. Pointing out problems at the earliest reduces the number of expensive revisions and enhances the overall quality of the product.
Roles of Advanced Materials in PCBA
Materials chosen for board assembly carry great import with regard to their specifying the final characteristics of strength and efficiency with which the product is to work. The few special high-performance substrates such as FR4, ceramic, or polyimide can all favorably qualify the product electrically in terms of insulation and thermal resistance, reducing their integrity in the long run and protecting the circuit from electromagnetic interference.
Miniaturization and Its Effect on PCB Assembly
However, the more these end devices shrink, the more complex they become, thus, forcing PCBA assembly to increase its narrowest space to take in miniature component devices. SMT and advanced solder technology allow use of high-density PC boards while ensuring they do not compromise normal performance. Miniaturization means the job is much more delicate and requires very advanced equipment and technicians.
Supply Chain Problems Facing PCB Manufacturing
A consistent supply chain also leads to good assembly of printed circuit boards. Production schedules are usually delayed due to unforeseen conditions like shortages in components, money value fluctuations of materials, or unexpected disruptions in logistics. Partnering with reputable suppliers and having an orderly inventory management scheme helps significantly in mitigating the backlog and ensuring continuity in PCB assembly.
Testing Beyond Functional Validation
Functional testing is the first level in checking that a given PC board assembly can operate well. However, many more tests are meant to improve reliability. Tests like thermal cycling and humidity exposure basically assess how well the assembly can perform under extreme environments. Mechanical stress tests measure durability over time to ensure that this PC board can handle its fair share of wear and tear. The further tests significantly increase product quality and durability.
Importance of PCB Design Software in Assembly
Indeed, modern PCB design software plays a real part in establishing an efficient line for assembling a PC board. Advanced designing features allow engineers now to specify extremely precise layouts and simulate circuit behavior to pinpoint potential errors well before actual manufacturing. Innovative functions like Design Rule Checks (DRC) and 3D visualization have all sought to optimize designs for better manufacturability. Assembly challenges will be fewer, and the productive efficiency that results will be great.
The Flexibility and Rigid-Flex of PCBs are on the Rise
Increased applications for devices worn on the body and medical electronics have increased demands on flexible and rigid-flex PCBs. This innovative style offers food for space and better protection compared to classical rigid boards. However, the PCBA circuit board assembly for flexible PCBs is further complicated by the specialized technologies required to guarantee reliability, such as low-stress soldering and very careful handling of fragile materials.
The Future of PCB Assembly Automation
Automation is steadily pushing forward into the assembly of printed circuit boards, realizing faster, less expensive production. Automated visual inspection aided by AI, robotic soldering, and defect detection through machine learning are improving accuracy and minimizing errors. While the industry focuses on smart manufacturing, automated processes will boost productivity, reduce human intervention, and boost the quality of PCB assemblies.
Best Practices in PCBA
Using best practices during PCBA circuit board assembly enhances a product in reliability and efficiency. Here are some recommendations:
• Component Selection: Select components compatible with PCB design and assembly process to minimize problems during manufacturing.
• Process Documentation: Detailed documentation of assembly procedures; ensure consistency and troubleshoot.
Final Conclude
Learning the steps and best practices in assembling printed circuit boards is critical to producing high-quality electronic devices. By ensuring attention in design reviews, incorporating precise assembly processes and quality controls, manufacturers can achieve good results in PCBA, which in turn lead to reliable and efficient products.
Get Your PCB Quote!