Medical PCBA Guide: Design, Process & Safety
From life-saving diagnostic devices to monitoring and therapeutic solutions, medical PCB assembly directly impacts patient safety and device effectiveness.
Get Your PCB Quote!
Table of Contents
- 1. מבוא: פעימות הלב של מכשור רפואי
- 2. מדוע הרכבת PCB רפואית דורשת דיוק ללא תחרות?
- 3. שיקולים מרכזיים בתכנון וייצור של PCBA רפואי
- 4. תהליך ה-PCBA הרפואי: מהקונספט ועד למכשיר
- 5. יישומים מגוונים של PCBA במכשירים רפואיים
- 6. בחירת יצרן הרכבות PCB רפואיות מתאים
- 7. PCB רפואי Aהרכבה שאלות נפוצותs
- 8. <br> סיכום
- המנות העיקריות
1. Introduction: The Heartbeat of Medical Devices
In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, medical devices are continually advancing, offering unparalleled diagnostic capabilities, therapeutic interventions, and patient monitoring solutions. At the core of virtually every one of these life-saving and life-enhancing innovations lies the Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA). However, unlike standard electronics,medical PCB assembly operates under an entirely different set of stringent requirements, making it a highly specialized field. This guide provides an essential overview of medical PCBA, exploring its critical importance, unique challenges, and the rigorous processes involved in bringing a reliable medical PCBA product to life.
2. Why Medical PCB Assembly Demands Unrivaled Precision?
The stakes in medical electronics are exceptionally high. A malfunctioning device can have severe, even fatal, consequences. This inherent risk drives the need for extraordinary precision, reliability, and adherence to strict regulatory standards in every stage of medical device assembly. Here’s why PCBA in medical devices is so unique:
- Regulatory Compliance:Devices must meet rigorous standards set by bodies like the FDA (U.S.), CE (Europe), and others. This includes ISO 13485 certification, which specifies requirements for a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices.
- Uncompromising Reliability:Medical devices often operate continuously, sometimes for years, within or on the human body. Failure is not an option. This demands components and assembly processes that ensure long-term, flawless performance.
- Patient Safety:Any electrical malfunction, component failure, or material interaction could pose a direct risk to patient health. Biocompatibility, sterility, and low-power consumption are often critical.
- Traceability:Every component, process step, and testing result must be meticulously documented and traceable. This is vital for quality control, recall management, and regulatory audits.
- Miniaturization and Density:Many modern medical devices, particularly wearables and implantables, require extremely compact and high-density PCBAs, pushing the boundaries of manufacturing capability.
3. Key Considerations in Medical PCBA Design and Manufacturing
Designing and manufacturing medical electronics assembly requires a holistic approach that factors in several critical aspects:
Material Selection
The choice of materials is paramount. Boards must often withstand harsh conditions, including sterilization processes, fluctuating temperatures, and even bodily fluids. Materials must be:
- Biocompatible:For devices that contact or are implanted within the body.
- Chemically Resistant:To withstand sterilization agents and cleaning solutions.
- Thermally Stable:To perform consistently across various operating temperatures.
- Low Outgassing:To prevent contamination, especially in sterile environments.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and Testability (DFT)
DFM and DFT are crucial from the outset. Medical devices often have complex designs and tight tolerances. Collaborating with a medical PCB assembly service early in the design phase can prevent costly revisions and ensure manufacturability and thorough testing capability.
Cleanliness and Environmental Control

Manufacturing medical PCBAs often requires controlled environments, such as cleanrooms, to prevent contamination from dust, particles, and other airborne substances that could compromise device integrity or patient safety.
Component Sourcing and Management
Only medical-grade, high-reliability components from approved suppliers are acceptable. Counterfeit components are a significant risk. A robust supply chain management system ensures authenticity, quality, and traceability.
4. The Medical PCBA Process: From Concept to Device
The journey of a medical PCBA product involves several intricate stages:
1) Design & Prototyping: Initial design, layout, and rapid prototyping to validate functionality and manufacturability, often incorporating DFM/DFT feedback.
2) Component Sourcing & Incoming Inspection: Procuring certified, high-quality components followed by rigorous inspection to verify specifications and authenticity.
3) PCB Fabrication: Manufacturing the bare PCB according to precise specifications and material requirements.
4) PCB Assembly:
Solder Paste Application: Applying solder paste with high precision to pads.
Component Placement (SMT & Through-hole): Automated placement of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) components and manual or automated insertion of Through-Hole Technology (THT) components.
Reflow Soldering & Wave Soldering: Melting and solidifying solder to create electrical and mechanical connections.
5) Inspection & Testing: Critical for ensuring flawless performance. This includes:
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): High-speed visual inspection for defects.
X-ray Inspection: For checking solder joints on hidden components (e.g., BGAs).
In-Circuit Test (ICT): Checks for shorts, opens, resistance, capacitance, and other basic electrical characteristics.
Functional Testing: Simulates the device’s real-world operation to verify performance.
Burn-in Testing: Subjecting the PCBA to extreme conditions to identify early failures.
6) Conformal Coating/Potting: Applying a protective layer to shield the PCBA from moisture, dust, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, enhancing durability.
7) Final Assembly & Packaging: Integrating the PCBA into the final device enclosure, followed by sterile packaging where required.
5. Diverse Applications of PCBA in Medical Devices
The versatility of PCBA in medical device technology is evident across a broad spectrum of healthcare applications:
- Diagnostic Imaging:Advanced PCBAs power MRI machines, CT scanners, ultrasound equipment, and X-ray systems, enabling high-resolution imaging.
- Monitoring Devices:From patient monitors in ICUs to wearable fitness trackers and glucose meters, PCBAs are central to collecting and interpreting vital health data.
- Therapeutic Devices:This category includes devices for pain management, drug delivery systems, and specialized equipment like PCBA in red light therapy devices, which require precise power control and timing.
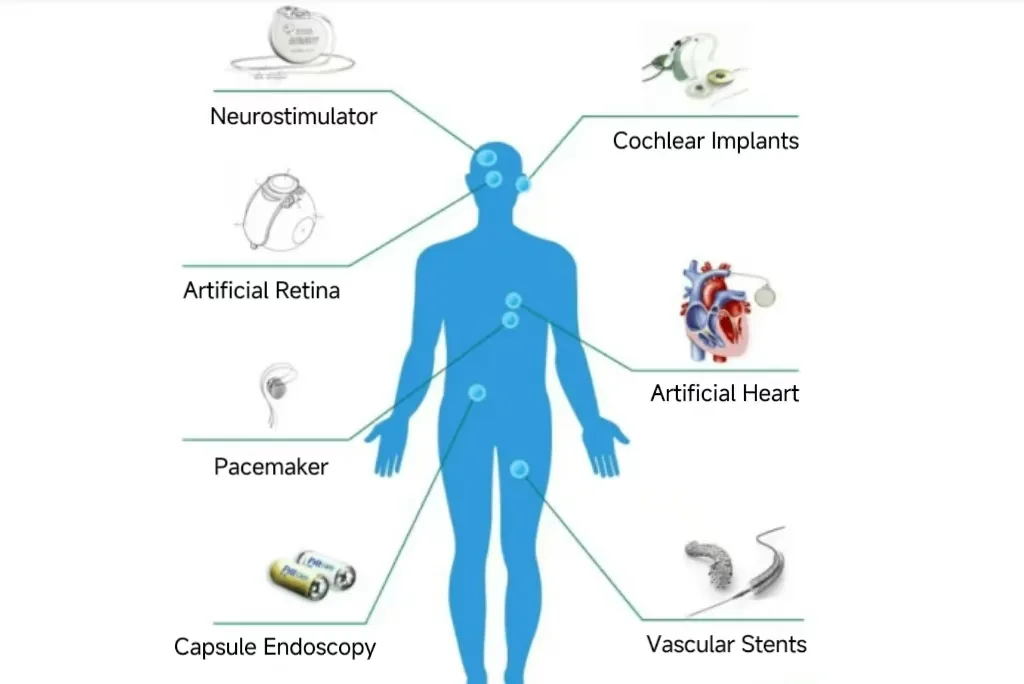
- Implantable Devices:Pacemakers, defibrillators, and neurostimulators rely on extremely miniaturized, ultra-reliable, and biocompatible PCBAs.
- Surgical Equipment:Robotic surgical systems, endoscopes, and electrosurgical units utilize complex PCBAs for precise control and functionality.
- Medical Alert Devices:PCBA in medical alert devices ensures reliable communication, GPS tracking, and robust battery life for emergency situations, often prioritizing durability and user-friendliness.
- Laboratory Equipment:Analyzers, centrifuges, and sequencers in medical laboratories depend on precise PCBAs for accurate and repeatable results.
6. Selecting the Right Medical PCB Assembly Manufacturer
Choosing a reliable medical PCB assembly manufacturer is perhaps the most crucial decision. A superior partner will offer more than just assembly; they offer expertise, compliance, and a commitment to quality. Key factors to consider include:
| Factor | Description | Benefit |
| Certifications | ISO 13485 certification is non-negotiable. Other relevant certifications include ISO 9001 and IPC standards. | Ensures adherence to quality management systems specific to medical devices. |
| Experience & Expertise | A proven track record in manufacturing complex medical-grade PCBAs and an understanding of specific medical device requirements. | Reduces risks, ensures efficient production, and provides valuable design insights. |
| Quality Control | Robust testing protocols (AOI, X-ray, ICT, Functional Test), rigorous inspection, and traceability systems. | Guarantees reliability, performance, and compliance with safety standards. |
| Supply Chain Management | Established relationships with reputable medical-grade component suppliers and strict counterfeit prevention measures. | Ensures genuine, high-quality components and mitigates supply risks. |
| Cleanroom Capabilities | Ability to assemble in controlled environments (e.g., Class 10,000 or 1,000 cleanrooms) when required. | Prevents contamination critical for certain medical devices. |
| Communication & Support | Transparent communication, dedicated project managers, and strong technical support throughout the entire project lifecycle. | Facilitates smooth collaboration and problem-solving. |
7. Medical PCB Assembly FAQs
The paramount importance of regulatory compliance (e.g., ISO 13485, FDA), uncompromising reliability, and patient safety requirements.
In red light therapy, PCBAs are crucial for precise control of LED arrays, managing power delivery, timing treatment cycles, and often incorporating safety features and user interfaces.
ISO 13485 is an internationally recognized standard for quality management systems in the medical device industry. It demonstrates a manufacturer’s commitment to meeting regulatory and customer requirements, which is crucial for market access and device safety.
8. Summary
Medical PCB assembly is a highly specialized and critical field within electronics manufacturing, demanding precision, rigorous quality control, and strict adherence to regulatory standards. From life-saving diagnostic equipment to patient monitoring and therapeutic solutions like PCBA in medical alert devices and PCBA in red light therapy devices, the integrity of the PCBA directly impacts patient safety and device effectiveness. Understanding the unique challenges, meticulous processes, and essential criteria for selecting an experienced medical PCB assembly manufacturer is paramount for bringing reliable, compliant, and innovative medical PCBA products to the healthcare market.
Key Takeaways
- Medical PCB assembly is fundamentally different from commercial PCBA due to strict regulatory compliance, reliability, and patient safety imperatives.
- Key considerations include specialized material selection, DFM/DFT, cleanroom manufacturing, and robust supply chain management for medical-grade components.
- The assembly process involves meticulous steps from design to comprehensive inspection and functional testing, often including protective coatings.
- PCBA is integral to a vast range of medical devices, from diagnostic imaging and surgical tools to wearables and implantables.
- Choosing an ISO 13485 certifiedmedical PCB assembly service with a proven track record, stringent quality control, and excellent communication is vital for project success.
Table of Contents
- 1. מבוא: פעימות הלב של מכשור רפואי
- 2. מדוע הרכבת PCB רפואית דורשת דיוק ללא תחרות?
- 3. שיקולים מרכזיים בתכנון וייצור של PCBA רפואי
- 4. תהליך ה-PCBA הרפואי: מהקונספט ועד למכשיר
- 5. יישומים מגוונים של PCBA במכשירים רפואיים
- 6. בחירת יצרן הרכבות PCB רפואיות מתאים
- 7. PCB רפואי Aהרכבה שאלות נפוצותs
- 8. <br> סיכום
- המנות העיקריות
Get Your PCB Quote!