Modern PCB Assembly: SMT, Through-Hole & Emerging Tech
Now let's learn more about the circuit card assembly and PCB board assembly in the modern electronics and how they are assembled
Get Your PCB Quote!
Table of Contents
- 1. Ole a le Circuit Card Assembly?
- 2. Komiti Fa'atonu Lolomi ma La Latou Matafaioi
- 3. Laasaga Autu i le Fono a le PCB Board
- 4. Fa'asagaga Mauga vs. Fonotaga Uo-Pu
- 5. Lu'i Faafeagai i Fonotaga
- 6. Tulaga Pulea ma Tofotofoga
- 7. Le Matafaioi a le Automation i aso nei Fonotaga
- 8. Fa'atekonolosi fa'atupu i le PCB Design
- 9. Aganuu vs. Mass Production
- 10. aotelega
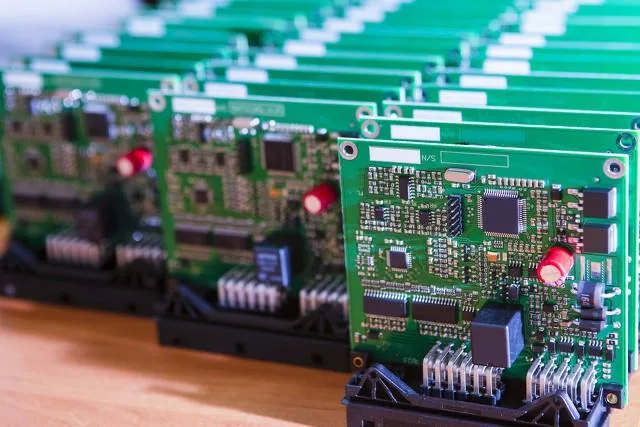
Electronics have changed from being bulky components and simple circuits. The gadgets today are slim, powerful, and ever decreasing in size. With circuit card assembly forming the basis of all such innovations, that is the crucial process which breathes life into modern electronics.
From the smartphone all the way to aerospace technology, circuit boards make it all work. How are they assembled, exactly? Let us now witness the manufacturing and assembly of the building blocks of modern technology.
1. What is Circuit Card Assembly?
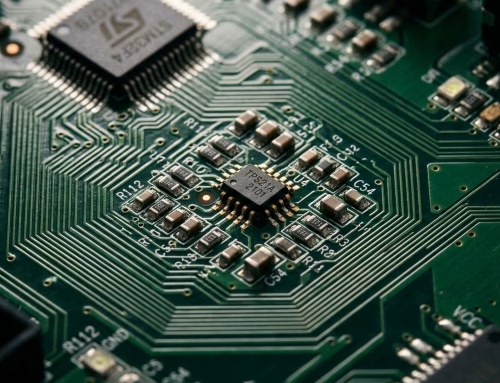
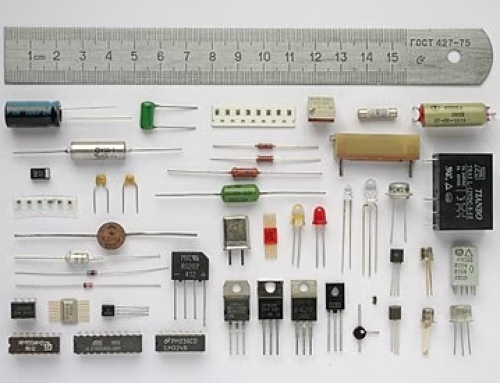
In this process, electronic components are attached to a card or board. This card is usually fabricated of non-conducting material and carved out with conductive pathways. These pathways serve to connect various parts in a device’s circuitry.
This process does not merely attach components. It must be done with a precision that ensures proper planning and clean execution. The product must prove reliable whether it is being used in a harsh environment to power a smartwatch or even just for the running of thousand servers.
2. Printed Circuit Boards and Their Role
PCBA is an acronym for printed circuit board assembly, which refers to the result of a board being built and all components being installed on top of it. The actual base board is referred to as a PCB, upon which all parts are placed.
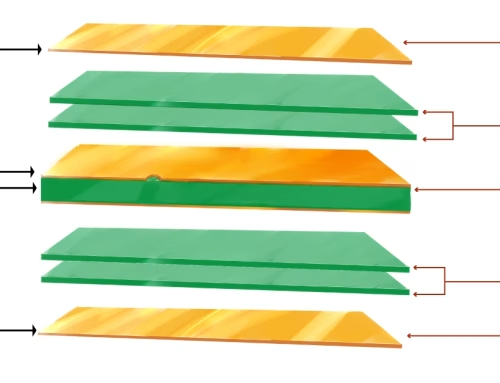
What distinguishes one board from another is its intricacy. Some PCB designs are single-sided with few components on them. Some are multilayer designs, intricately routed for faster speeds and higher power.
Keeping in mind that designing a PCB entail being careful about heat, electrical noise, and spatial constraints, this stage can ensure the end product being either good or bad.
3. Core Steps in PCB Board Assembly

There exist several intermediate steps the PCB board assembly process carries through before making the final product. After being first applied with soldering paste, the soldering process follows. Such paste gets applied in areas where components will sit.
When placing components onto the card, the operation is done by high-speed pick-and-place machines. After placement, the board enters reflow soldering, where the solder paste is melted to hold all parts in place.
After that, the board is inspected. Quality control is essential here. Any error in placement or connecting will lead to the failure of the device.
4. Surface Mount vs. Through-Hole Assembly
Everything is not installed in the same way because of some differences in some components. Surface mount technology places parts right on the surface of the board. Being faster and more flexible, it is the commonly used method today.
However, some situations require the use of through-hole technology, wherein component leads insert into holes drilled in the board and then get soldered on the opposite side. This is necessary when the assembly must carry a greater weight, such as in military and aerospace applications.
Very often, a hybrid approach is used. Boards may contain SMT, as well as through-hole parts, depending on design requirements and performance objectives.
5. Challenges Faced in Assembly
Every production line faces unique challenges. Miniaturisation is one of the defining aces of circuit board assembly. As the device will become smaller, the components will too. This requires greater precision and high-end tooling.
Another fairly common problem faced would be heat. During reflow soldering, the board goes through high-temperature stages, and if it is a little hard for the entire process, some components will suffer damages and defects will be detected in soldering.
Electromagnetic interferences (EMI) are also becoming a great concern. Poor design or assembly can introduce signal noise. This affects performance, especially in high-speed circuits.
6. Quality Control and Testing

No assembly is trustworthy unless it has undergone stringent testing. Testing occurs at the printed circuit board assembly stage. From visual inspection to in-circuit testing.
Functional testing is a must. It verifies whether a final board performs to specifications or not. Those that do not meet these tests are either reworked or scrapped.
Generally, companies go for automated processes as it will promote speed and consistency. Then again, human inspection is, for some scenarios, necessary, especially for custom boards with high values.
7. The Role of Automation in Modern Assembly
Automation redefined the way boards are manufactured. Nowadays, placement, soldering, and testing are all achieved using high-speed machines. This results in faster production and lesser errors.
With this, however, design becomes all the more critical. Automations will do exactly what they are told. If the layout is flawed, even the most efficient assembly machines are not going to save the process.
Software tools provide assistance to designers in the layout of paths, component selection, and performance simulation. They help close the gap between the design and manufacturing processes.
8. Emerging Technologies in PCB Design
The future in printed circuit board assembly seems promising. These flexible PCB now find applications in wearables and flip phones. They bend and twist without snapping.
Another new technology is 3D printing. Hence, there are companies that are 3D printing entire circuit arrangements, which eliminate some steps and materials. This technology is still under the evolving stage; however, it does have a lot of potential.
Another new technology is chip-on-board technology for miniaturisation, which means bare silicon chips are placed directly on the PCB. It does reduce space and provide performance, especially in areas where high speed is essential.
9. Custom vs. Mass Production

Mass production is all about volumes and consistency. But in some sectors, custom boards are required. These cater to peculiar requirements, such as scientific equipment or advanced research.
There is more time consumed in custom PCB board assembly and in addition it costs more per unit than the usual assembly. But it gives you that extra favourability in design and performance; it lets engineers think out of the box without the restriction of the standard designs.
They go together because custom assembly and mass assembly both have their corresponding places. The outcome, scenario, and budget base would really steer one way or the other.
10. Summary
With the advancement of technology, the electronic world is forever in changes regarding printed circuit board assembly. Working with new materials, quicker machines, and clean processes promotes the modern electronic manufacturing.
The quickest ones to adapt have the future. In the market, the ones that invest in designing, testing, and quality will differentiate themselves.
The changing times demand that one learns this art, whether a new setup or a seasoned manufacturer. In essence, it is not just assembly anymore. It is the very base of our digital world.
Table of Contents
- 1. Ole a le Circuit Card Assembly?
- 2. Komiti Fa'atonu Lolomi ma La Latou Matafaioi
- 3. Laasaga Autu i le Fono a le PCB Board
- 4. Fa'asagaga Mauga vs. Fonotaga Uo-Pu
- 5. Lu'i Faafeagai i Fonotaga
- 6. Tulaga Pulea ma Tofotofoga
- 7. Le Matafaioi a le Automation i aso nei Fonotaga
- 8. Fa'atekonolosi fa'atupu i le PCB Design
- 9. Aganuu vs. Mass Production
- 10. aotelega
Get Your PCB Quote!