A Complete Guide to Flexible PCB Assembly
Flexible PCB assembly enables bendable electronics via precise SMT processes, rigid-flex hybrids, and advanced materials for compact, durable designs.
Get Your PCB Quote!
Table of Contents
You know how everything’s getting smaller these days? Phones, watches, even medical stuff. And inside all of that, there’s a board, right? Not the stiff kind. I’m talking about the ones that fold, bend, curl around a curve without snapping in half. That’s a flexible PCB.
I’ve had to explain this to a few people, and the easiest way I put it is, it’s like the nervous system of modern tech, but way more cooperative. If you’ve ever heard someone mention flex pcb assembly, they’re talking about how these bendy boards get built. And yeah, it’s a real process. It’s not like just soldering stuff on a plastic sheet and calling it a day.
We’ll go into all of that here. What makes these boards work, why china flex pcb assembly is such a thing now, and how flex circuit assemblies end up inside your gear without you even realizing it.
1. What Is Flexible PCB Assembly?
Okay, so here’s the deal. A flexible PCB is basically a circuit board that… doesn’t act like a board. You can twist it, fold it, fit it into spaces where rigid ones would snap like a cracker. Sounds cool? It is. But that also means putting them together, assembling them, is a bit more of a dance.
See, in flexible pcb assembly, you’re not just dealing with regular copper on fiberglass. You’ve got polyimide and other materials that can stretch or warp if things get too hot or too rough. That’s where pcb assembly flexible comes into play, everything needs to move and stay functional.
Now, I’ve seen people try to treat them like rigid boards. Doesn’t end well. Cracks. Bad connections. You name it. But when it’s done right? These boards go into medical gear, wearable tech, automotive dashboards, anywhere space is tight but performance still matters.
Honestly, I didn’t even realise how common flex circuit assemblies were until I opened up my fitness tracker. It’s all packed in so tight, yet somehow nothing’s disconnected. That’s the magic of good assembly. Tight spaces, strong bonds, no room for errors.
You can think of it like the difference between a hardcover book and a rolled-up magazine. One stays flat no matter what. the other adapts to wherever you put it. That adaptability makes flex PCBs perfect for things like hearing aids, foldable phones, and even small satellites, where space isn’t just limited. it’s non-existent.
2. The Flex PCB Assembly Process (It’s Trickier Than You Think)
The flex pcb assembly process isn’t just a carbon copy of rigid board manufacturing. There’s a bit more finesse involved, more moving parts, literally and figuratively.
Here’s how it usually goes:
2.1 Material Prep
You’re not dealing with stiff boards anymore. Flex PCBs need layers that bend but don’t break. Typical stack:
Copper foil (very thin, very delicate);
Polyimide (flexible, heat-resistant);
Sometimes PET (cheaper but less heat-tolerant).
You laminate these together carefully. If there’s a wrinkle or bubble? That’s a failed board right there.
2.2 Design with Movement in Mind
This is where most early mistakes happen.
Traces should curve, not turn at sharp angles;
Bend zones need space, no pads or vias in the danger zone;
Don’t pack components too close to folds.
This part isn’t about cramming as much as possible. It’s about letting the board breathe.
2.3 SMT Assembly (Surface-Mount Tech)
Now we add the brains.
The flex pcb smt assembly phase uses pick-and-place machines, but with adjusted handling:
Lower pressure to avoid damaging the thin substrate;
Tighter reflow profiles (too much heat = deformation);
Support plates or frames to keep the board flat during soldering.
Every step is dialed in. Flex boards won’t survive the “close enough” mindset.
2.4 Layering & Laminating (for Multi–layer Boards)
A lot of flex circuit assemblies are multi-layer, which means:
More adhesive layers;
More time in the press;
More chances to mess it up.
Alignment is everything. If one layer shifts, even slightly, the whole circuit could short, warp, or tear under stress.
That’s the core of the process. It’s slow, careful, and unforgiving, but if it’s done right, the final board will fold neatly into a hinge, wrap around a curve, or tuck inside a wearable device like it was made for it. Because it was.
One common issue? Tombstoning, where small components like resistors pop up on one side during reflow. It happens when the heat distribution isn’t perfectly balanced. On a flex board, which already warps under pressure, the risk is even higher. That’s why most flex pcb smt assembly lines use support fixtures or jigs to hold everything flat.
3. Rigid-Flex PCB Assembly and Manufacturing
Here’s where things get interesting. Imagine combining the best parts of both worlds, the sturdy, dependable base of a rigid board and the bendy, adaptable traits of a flex circuit. That’s a rigid-flex PCB. And no, it’s not just two boards taped together. It’s one, fully integrated structure.
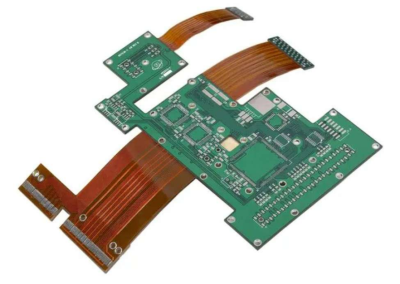
A rigid-flex design has solid sections (where you usually mount the components) connected by flexible strips that can bend and fold to fit into oddly shaped spaces. These are the go-to choice for industries that need compact, reliable electronics, aerospace, medical devices, defense systems, even next-gen consumer gadgets.
What makes them so appealing?
Well, you get strength where it counts. Components stay anchored to the rigid parts, which are stable and don’t flex. But you also get flexibility where it’s needed, the connecting sections can twist and fold inside cramped housings without the need for bulky connectors or fragile ribbon cables. That’s fewer failure points, better signal integrity, and cleaner packaging overall.
The rigid flex pcb assembly process itself is a bit more involved than working with just flex or rigid boards. You’re laminating multiple layers together, alternating between rigid materials like FR4 and flexible layers like polyimide. And it all needs to be aligned perfectly. We’re talking microns of tolerance. If anything shifts, you’re looking at stress fractures, conductivity issues, or layers that just don’t line up.
Then comes rigid flex pcb manufacturing, which includes drilling, plating, imaging, etching, the works. Each layer gets treated differently depending on whether it’s part of the rigid section or the flex zone. That’s where the cost creeps in. You need manufacturers who specialize in these hybrids because a regular PCB shop might not have the setup to get this right.
In short: rigid-flex boards are more complex, yes. But if you want fewer connection points, cleaner internal design, and a board that can literally bend around your problems, this is what you go for.
4. China Flex PCB Assembly Process, Why It Leads the Market
There’s no getting around it, if you’ve looked into getting a flex PCB made, you’ve probably ended up on a Chinese manufacturer’s website. That’s not a coincidence. China flex pcb assembly is everywhere for a reason.
Actually, several reasons.
First off, scale. Chinese factories don’t just make a few batches here and there, they’re producing flexible pcb assembly units by the thousands daily. That kind of volume brings costs way down. But it’s not just about price. The tech is there too. Some of the most advanced flex pcb smt assembly lines are running out of Shenzhen, with automation, inspection systems, and materials on par with global standards.
Then there’s speed. Once you finalize a design, many of these companies can move into production almost immediately. That’s a big win if your timeline’s tight.
But it’s not all plug-and-play. Some manufacturers overpromise, others cut corners. That’s why picking the right china flex pcb assembly partner matters more than people think.
The best ones:
Have actual engineers you can talk to;
Provide DFM feedback before printing;
Offer traceability, testing, and quality reports without being asked.
The cheaper options? They’ll run your file as-is, flaws and all, and you’ll find out when your boards arrive with lifted pads or bad vias.
So yes, China leads. But picking the right shop still takes some legwork.
5. Working with a Flex PCB Manufacturer
You’d think once you pick a manufacturer, everything just flows. Not quite. Choosing a flex pcb manufacturer, especially for anything more complex than a single-layer board, is half technical, half detective work.
Start by checking capabilities. Can they handle multi-layer pcb assembly flexible builds? What’s their track record with rigid flex pcb assembly? If you need special materials or odd shapes, do they have experience with that?
Then ask for examples. Any serious flex pcb manufacturer should be able to show off past projects, not just pictures, but yields, turnaround times, maybe even test reports. If they hesitate? Red flag.
Also, look at how they communicate. Some shops respond instantly and actually review your files. Others send templated replies that don’t answer anything. The good ones ask questions. They challenge unclear designs. They tell you when something might break.
And please, don’t skip testing. Whether it’s basic continuity or full electrical testing, you want it done before they ship. It’s a lot easier to catch bad soldering or shorts while the boards are still on their floor, not yours.
The takeaway: working with a good flex pcb manufacturer saves you time, money, and a whole lot of stress. But only if you vet them properly first.
And don’t assume all testing means the same thing. Ask if they do flying probe testing, impedance checks, or thermal cycling. A good flex pcb manufacturer will walk you through what’s included, and what costs extra. Always check the fine print.
6. Design & Assembly Tips for Better Flex PCBs
If there’s one place where most flex designs go sideways, it’s in the early planning stage. Not the materials. Not the tools. The design.
See, flexible pcb assembly isn’t just about building something that works. It’s about building something that holds up, through folding, heat, vibration, all of it. That takes planning.
A few tips that save a lot of headaches:
Never put pads or vias in bend zones. That’s the fastest way to tear a trace clean off.
Keep your bends wide. Sharp folds are cool in paper origami, not so much in PCBs.
Stagger your traces. Especially on multiple layers, you want even stress distribution.
Also, if you’re doing pcb assembly flexible work, watch how you’re placing components near the edges. Stuff too close to the flex junction tends to crack or peel over time. Not always right away, but give it a few thermal cycles and things get ugly.
And don’t overlook the basics:
Use fillets at corners;
Avoid 90-degree trace turns;
Include strain relief where needed;
Test your design in 3D, not just in your head.
Some of this sounds simple, but you’d be surprised how many failed flex circuit assemblies start from careless layouts. If you’re outsourcing, make sure your flex pcb manufacturer flags any red flags before production. If they don’t? That’s a red flag on its own.
The better your design, the easier the assembly. And the fewer surprises when you finally power it up.
7. The Future of Flexible PCBs and Assembly Technology
Flex PCBs aren’t just for weird-shaped gadgets anymore. They’re quietly becoming the foundation of the next generation of tech.
We’re talking thinner, faster, more rugged. The kind of stuff that doesn’t just fold, it bends dozens of times a day and still works like nothing happened.
Here’s what’s coming:
Wearables are exploding. Smart glasses, AR devices, health patches, all powered by flexible pcb assembly;
Flexible sensors are showing up in industries from fitness to automotive;
High-speed signal routing on flex boards is finally viable, thanks to better materials and design tools;
And AI? It’s not just for end-user products, it’s helping optimize the flex pcb assembly process itself, making inspections smarter and builds more consistent.
Even rigid flex pcb manufacturing is evolving. What used to take multiple manual steps can now be handled by semi-automated lines, with higher tolerances and fewer defects.
And yes, China flex pcb assembly shops are leading that charge, investing in equipment, automation, and talent to scale even faster.
The point is: if you’re working in hardware design or electronics manufacturing, ignoring flex tech now is like ignoring surface-mount in the nineties. It’s not the future. It’s already here.
We’re even seeing experiments with implantable electronics that monitor vital signs or deliver medication, all powered by ultra-thin flex boards. As materials improve, the line between electronics and biology keeps getting blurrier.
8. Flexible PCB Assembly FAQs
It’s the process of building circuit boards that can bend, twist, and fold, unlike rigid boards. It involves special materials like polyimide, tighter tolerances, and techniques that account for movement and stress.
Flex PCBs are entirely bendable, while rigid-flex boards combine solid and flexible sections. Rigid-flex designs are great for complex shapes, folding enclosures, and reducing connectors.
China has the scale, speed, and equipment to handle massive flex PCB orders. Many manufacturers also offer competitive pricing, fast turnarounds, and advanced automation.
Putting pads in bend zones, using sharp trace corners, skipping strain relief, or underestimating how thermal stress can affect layout, all of these lead to failures. Planning ahead is everything.
aLook for shops with a track record in pcb assembly flexible, ask for examples, check communication quality, and make sure they include real testing, not just a basic visual inspection.
It can be, especially for rigid flex pcb manufacturing, but the long-term benefits, reduced failure points, saved space, and better reliability, usually outweigh the upfront cost.
Expect more wearable tech, smarter medical devices, and AI-assisted manufacturing. Flex boards are already showing up in high-speed applications and even implantable electronics.
9. Summary
Flexible PCBs aren’t just clever, they’re essential. From wearables to satellites, they let electronics fit into smaller, tighter, more complex spaces. This guide breaks down how flex pcb assembly works, what makes rigid-flex designs special, and why China flex pcb assembly dominates the market.
It covers everything from materials and layouts to SMT techniques and design mistakes to avoid. You’ll also learn how to vet a flex pcb manufacturer, what testing really means, and where the tech is heading, like AI-optimized lines and even implantable devices. If you build hardware, this isn’t just good to know, it’s need-to-know.
Table of Contents
Get Your PCB Quote!