Complete Guide to Flex PCBs Assembly Progress
Flex PCBs enable bendable, lightweight electronics with high integration, used in wearables, medical, automotive, and aerospace, despite higher costs.
Get Your PCB Quote!
Table of Contents
- 1.Что такое гибкая печатная плата?
- 2.Что такое сборка гибкой печатной платы?
- 3.Выбор материала для сборки гибкой печатной платы
- 4. Каковы основные процессы сборки гибких печатных плат?
- 5.Каковы преимущества гибкой сборки печатных плат?
- 6. Какие проблемы возникают при использовании Flex PCBA?
- 7. Каковы области применения Flex PCBA?
- 8. Часто задаваемые вопросы по гибким печатным платам
- 9.Summary
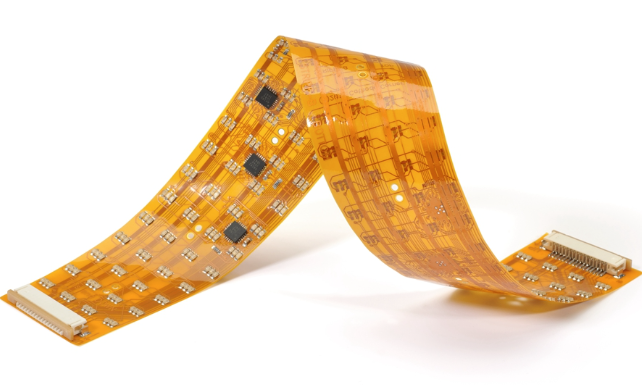
Can you bend a printed circuit board at will? The answer is yes, but only for flex PCBs. At this point you may ask, what is the role of Flexible PCB? Its role is unparalleled. It can fit the curvature of the electronic device you want. The rise of Flexible PCB assembly has brought new momentum to the electronics industry’s rapid advancement.
This article explores the critical steps in Flexible PCB assembly.We will also discuss Flex PCB assembly advantages, challenges, and applications trends. Let’s explore the dynamic landscape of Flex PCB Assembly.
1.What is Flex PCB?
Flexible PCBs, also known as flex boards or flex circuits, are made with thin laminates that are bendable, have high tensile strengths, and are flexible. These boards can be found on smartwatches and in medical equipment. They are distinguished by their ability to bend and twist.
2.What is Flex PCB assembly?
The process of mounting electronic components and soldering them onto a flexible printed circuit board (PCB) is called Flex PCB Assembly. Flex PCBs differ from rigid PCBs in that they are made of flexible materials. These materials are typically polyester or polyimide, which allows them to bend and fold to conform to different shapes.
3.Flex PCB Assembly Material Selection
Let’s consider some of the key materials used for Flexible PCB assembly. When building one of these boards, we need a substrate material, cover layer material, metal conductor layer material and adhesive.
As base substrates of flexible PCBs, polymide tends to be popular choice due to its superior thermal resistance. We also choose polyester for its low costs in imple lower temperatures. Polymide can act as the cover layer protecting circuitry while polyester provides additional flexibility. We may also utilize other materials like PEN thin FR4 as base substrates.
4.What are the Key Processes of Flex PCB Assembly
4.1 FPC Fabrication
Make sure that the fabrication of flexible printed circuit boards meets the design specifications. Check the quality of the bare Flex PCBs.
4.2 Component Preparation
We should create a detailed list of components, materials, and specifications. All components must be compatible with the Flex PCB assembly. We can coat component leads with solder to improve adhesion through pre-tinning.
4.3 Flexible PCB Baking
The stack of flex circuit boards is then sent through the baking process in order to reduce the moisture inside the board. The PCB thickness determines the temperature and duration of baking.

4.4 Flex PCB Fixture
Use a custom-designed assembly jig to fix the FPC in a specific position. This can effectively prevent the FPC from curling.
4.5 Soldering Paste Printing
After baking, the board is printed with solder paste. A squeegee is used to apply solder paste. It passes through the paste and then distributes in the ‘apertures” of the stencil that contains the board patterns. Solder paste must be applied with a consistent volume and aligned to avoid excessive, lackluster, or misaligned solder paste. FPC has special requirements for printed solder paste. Solder paste printing must be easy. It should have good thixotropy and it must adhere firmly to FPC.
4.6 Silkscreen Printing
PCB engineers create pathways of insulation ink onto the circuit. This helps to identify test points, warning signs, and components. This process is optional.
4.7 Component Mounting
We use high-precision machines with vision systems to align components on flexible substrates. The component will self-align during the reflowing process, even if it is slightly misaligned during the pick-and-place. The Flexible PCBA may have process defects such as solder balling and misaligned or missing components.
Even if there is slight misalignment during pick-and-place, the component has self-alignment properties during the succeeding reflow process. Flexible PCBA can incur process defects during component placement such as tombstoning, solder balling, and misaligned and missing components.
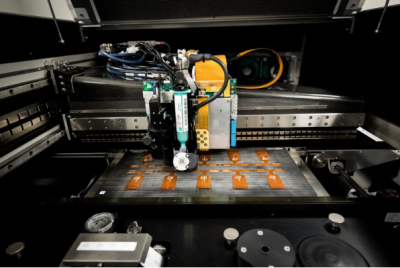
4.8 Reflow Soldering
Solder paste is used to adhere the components to the flexible board. Solder paste is melted during the reflow-soldering process, and then cooled to form a solid solder joint. Reflow ovens are used for this. There are different heating zones in these ovens. The temperature of each heating zone is set according to the solder profiles used in the assembly process.
4.9 Thermal Lamination
This is the step where we will apply any additional layers or coatings. Thermal lamination is used to secure layers.
4.10 Testing
The next step is to check if the FPCB functions according to the test specifications.
(1)AOI: Flexible PCBAs are also subjected to AOI. This is done in the same way as rigid boards. It verifies that components have been placed correctly on the circuit board. Cameras are used in automated optical inspection machines to detect issues such as misaligned or mispositioned components, and soldering problems like solder balls and shorting.
(2)X-ray Inspection: An X-ray inspection with automated software is performed to check the quality and thickness of the solder paste. The X-ray machine is useful in detecting reflow problems immediately.
(3)ICT: The machine is used to test for short circuits and open circuits as well as the welding condition of various parts.
(4)FCT: This functional test tests the flex boards under simulated working conditions to determine if they will function in different design states.
(5)Flying Probe Testing: It uses moveable probes to test the nets on the Flex PCB.
(6)Visual inspection: Manual inspection for defects such as cracks, damage, or discoloration.
(7)Flex Testing: Simulate bending cycles to ensure durability.
After testing, the flex board is removed from the panel and sent for final quality control (FQC). The circuit board is then sent to packaging and storage after FQC.
5.What are the advantages of Flex PCB Assembly?
(1)Extreme Flexibility: The Flexible PCBA can withstand dynamic bending, folding, or even twisting to fit complex 3D spaces.
(2)Lightweight Design: The cross-section of Flexible PCBA is ultra-thin and lightweight. This characteristic makes it ideal for wearables (smartwatch battery flex cables) and drones (lightweight sensor boards).
(3)High Integration: The circuit density of the Flexible PCBs is low. They integrate sensors, antennas, and thermal layers. They conform to device contours and maximize the space utilization of compact devices. And they realize “board-as-a-system” designs.
(4)Environmental Adaptability and Longevity: The substrate of Flex PCB performs well in a wide temperature range. This makes it suitable for high-accuracy industries. Its coverlays can provide moisture, dust, and corrosion protection. This extends its lifespan in wet/high-dust settings. Flex PCB integrated design, no moving parts. This makes it very wear-resistant and can be bent repeatedly.
6.What are the challenges of Flex PCBA?
Despite the significant advantages, flexible PCB assembly also has the following challenges:
(1)High assembly cost: The cost of materials (such as PI) and processes (such as multi-layer lamination) makes FPC assembly pricier than rigid PCBs.
(2)Difficult to repair: The components are densely packed and the substrate is fragile. That means manual soldering requires special fixtures.
(3)Heat dissipation limitation: The heat dissipation capacity of pure flexible structures is weak. We need to optimize through metal substrates or thermal vias.
7.What are the applications of Flex PCBA?

Flex PCBA combines the adaptability of flexible circuits with electronic component integration. It enables innovative solutions across industries.
(1)Consumer Electronics
It is usually used in Foldable & Flexible devices, Wearable Tech, and Wearless Earbuds.
(2)Medical Devices
It is often applied in Pacemakers/Implantable sensors, Endoscopes & Laparoscopic Tools, and Wearable Medical Monitors.
(3)Automotive and Transportation
It is widely used in ADAS Sensors, EV Battery Management Systems, and In-Cabin Electronics.
(4)Aerospace and Defense
It is largely applied in Satellites & Spacecraft, and Military Electronics.
(5)Industrial and Robotics
It is suitable for Robotic Arms & Cobots, Industrial Sensors & IoT Devices, and LED Lighting & Display Systems.
(6)Emerging Technologies
Electronic Skin (e-Skin) & Soft Robotics: Stretchable flex PCBs with embedded strain gauges mimic human touch. It can be used in prosthetics and soft robotic grippers for delicate object manipulation.
Energy Harvesting Devices: Flex PCBs in solar-powered wearables integrate flexible solar panels and energy storage. They can bend freely with the device without cracking.
3D-Printed Electronics: Hybrid flex-rigid PCBs combined with 3D-printed enclosures create custom-shaped devices. They are ideal for making medical implants and aerospace prototypes. This also reduces manufacturing lead times.
8.Flexible PCBA FAQs
Yes. We can repair via micro-soldering or modular component replacement. Though, complex multiple boards are challenging.
Flex PCB assembly uses bendable substrates, specialized lamination, and stress-relief designs; while rigid focuses on stability.
There are nine points. Material selection, Bend Radius, Component & Stiffeners Placement, Trace Routing & Layer Stackup, Thermal Management, Mechanical Anchoring & Strain Relief, Manufacturing Tolerances, Testing & Validation, and Cost Optimization.
Flexible PCB Manufacturing: Produce bare boards. It is the manufacture of circuit carriers.
Flexible PCB Assembly: Give bare board functionality. It is a key step in electronic system integration.
Solder paste printing must be easy. It should have good thixotropy and it must adhere firmly to FPC.
They are usually classified into single-sided, double-sided, multi-layered boards, and rigid-flex PCBs.
Yes. But it requires careful design modifications. Because it is less common than SMT due to the inherent challenges of working with flexible materials.
While conformal coating is not universally required for every flex PCB, it is highly recommended for most practical applications due to the inherent vulnerabilities of flexible substrates in real-world environments.
Yes. Especially in harsh environments due to the inherent vulnerabilities of Flexible PCB.
9.Summary
Flex PCBs have changed the way we use technology. They can power your gadgets, or help doctors with medical devices.
They are on a mission to make our devices and lives smarter. Contact Orinew if you need any assistance with the Flex PCB or Flex PCB assembly service.
Table of Contents
- 1.Что такое гибкая печатная плата?
- 2.Что такое сборка гибкой печатной платы?
- 3.Выбор материала для сборки гибкой печатной платы
- 4. Каковы основные процессы сборки гибких печатных плат?
- 5.Каковы преимущества гибкой сборки печатных плат?
- 6. Какие проблемы возникают при использовании Flex PCBA?
- 7. Каковы области применения Flex PCBA?
- 8. Часто задаваемые вопросы по гибким печатным платам
- 9.Summary
Get Your PCB Quote!