Flexible PCBs and the Future of Circuit Board Design: What Manufacturers Want You to Know
Flexible PCBs enable bendable electronics, offering space/weight savings, design freedom & applications in wearables, medical & automotive industries.
Get Your PCB Quote!
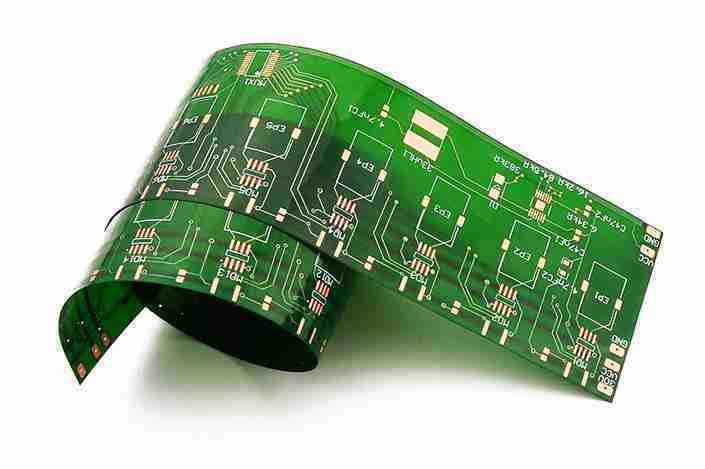
The production and design of printed circuit boards (PCBs) play an essential part in bringing new solutions in today’s rapidly-changing electronic industry. Flexible printed circuit boards represent cutting-edge technology which alters electronic design and operational methods. Designers, engineers, and users should be aware of the new characteristics that are inherent to Flexible PCBs and their future possibilities. PCB manufacturers are the PCB maker community has a wealth of information on how these breakthroughs influence the direction in PCB circuit board design.
Understanding Flexible PCBs: What Are They?
The traditional printed circuit board comprise of rigid, flat panels made out of conductive lines and layered with insulating materials that be the main design of electronics. PCBs, also referred to as flex circuits make use of lightweight, flexible substrates like polyimide which allow that the board be bent and folded without suffering any damage.
Flexible electronic designs permit incorporation into shapes and spaces that were previously unpractical. PCBs enable use in compact and adaptable 3D assemblies, wearable technology applications, foldable devices, and medical instruments unlike rigid PCBs.
Key Advantages of PCBs
Flexible printed circuit boards provide numerous benefits beyond their ability to bend which makes them ideal for today’s electronics manufacturers.
1.Space and Weight Reduction
PCBs are designed to reduce both the weight and size in electronic equipment. The light and thin PCBs’ materials enable designers to add additional features to small devices like smartphones and tablets.
2.Simplified Assembly and Improved Performance
Flexible circuits function as replacements for both rigid boards and connecting wires which simplifies the assembly process while enhancing signal performance. Device performance improves because there are fewer failure points when connectors and solder joints are reduced.
3.Design Freedom and Innovation
Flexible substrates grant engineers enhanced design possibilities to push innovation boundaries. Flexible substrates enable engineers to design innovative product shapes that rigid boards cannot accomplish such as foldable smartphones, curved wearable sensors, and embedded electronics in garments.
What PCB Manufacturers Want You to Know
With flexible printed circuit boards becoming increasingly popular, manufacturers stress important aspects that both customers and designers need to understand.
1.Material Selection Is Critical
Not all flexible materials are created equal. Polyimide serves as the primary substrate choice because of its superior thermal resistance alongside its electrical insulating properties. Manufacturers provide alternative materials based on specific thermal, mechanical and chemical needs for each application.
2.Design Complexity Requires Expertise
The creation of a PCB requires specific expertise along with specialized equipment. Careful planning of bending radii, conductor layout, layer stacking and strain relief features is essential to prevent mechanical failure. Early collaboration with an experienced manufacturer during product design helps achieve reliability and performance standards.
3.Cost Considerations
The upfront costs of PCBs exceed those of traditional rigid boards but they provide savings through better size efficiency, assembly improvements, and enhanced durability.
4.Testing and Quality Assurance
PCBs must undergo extensive testing under mechanical stress conditions because of their special properties alongside electrical examination. Modern inspection methods, such as the automated optical inspection (AOI) and the analysis of X-rays, and functional tests permit top manufacturers to guarantee the quality of their products.
Applications Driving the Growth of PCB

The expansion of PCB demand results from multiple industries advancing their product design and performance capabilities.
1.Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronics, such as smartwatches that fold and foldable smartphones and wireless earbuds are significant markets for PCB use. Manufacturers integrate flexible circuits into their products in order to make smaller and lighter devices that have more ergonomics and an improved user experience.
2.Medical Devices
PCB technology improves the performance of wearable health monitors and implantable devices along with portable diagnostic equipment. The biocompatibility and lightweight nature of flexible circuits combined with their body contouring ability makes them perfect for medical uses.
3.Automotive and Aerospace
Modern vehicles and aircraft integrate PCBs for sensor systems and controls and in lighting modules. PCBs offer vibration and temperature resistance that meets reliability requirements across these industries while allowing electronic assemblies to remain compact.
4.Industrial and IoT Devices
Flexible printed circuit boards empower smart sensors and connected devices to function in severe environments. The ability of PCBs to integrate into complicated shapes and confined areas proves essential for industrial automation and IoT applications.
The Future of PCB Circuit Board Design
The advancement of technology leads to a future in board design that increasingly depends on advanced manufacturing methods alongside flexible materials. Here’s what to expect:
1.Integration with Advanced Materials and Technologies
Future flexible printed circuit boards will integrate new conductive inks along with stretchable electronics and embedded components to improve their performance. The combination of flexible substrates with printed electronics and micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) will expand the boundaries of technological achievements.
2.Smarter, More Adaptive Devices
Flexible PCBs are expected to play a key part in the creation of devices that can be adapted to the changing needs of users or the changing environmental conditions. Imagine tablets that fold down into laptops, and clothes with built-in health monitoring features.
3.Sustainable Manufacturing
Environmental concerns are on the rise and makes manufacturers more inclined to adopt environmentally friendly production methods which use recyclable materials and techniques to minimize waste. The flexible printed circuit board permit manufacturers to reduce the quantity of materials they use while maximizing efficiency of energy throughout the process of assembly.
4.Customization and Rapid Prototyping
Advanced computer-aided design (CAD) combined with manufacturing automation will enable quick and affordable production of customized PCBs solutions as standard practice. The ability to adapt swiftly will enable quick product innovation along with accelerated market entry for new electronic devices.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer
The selection of a trustworthy manufacturer plays a crucial role in fully harnessing PCBs advantages. Select manufacturers that demonstrate expertise in flexible circuit production and maintain strict quality control procedures while delivering collaborative design assistance. Clear documentation of material sourcing procedures and testing protocols alongside proper certifications guarantees that PCBs projects achieve compliance with technical and regulatory requirements.
PCBs can be a game changer in the field of electronics manufacturing since they enable designers to design products that are more creative yet still maintain their compactness and strength. Designers can use the advanced materials provided by manufacturers who are innovative to design products that satisfy both aesthetic requirements and functional requirements.
Professionals with experience provide insightful advice and reliable solutions that are crucial to PCB and circuit design success.
Get Your PCB Quote!