Copper Clad Laminate (CCL): Everything you need to know
Understanding the composition of copper clad laminates and the features of different materials is the basis for PCB design, selection and manufacturing.
Get Your PCB Quote!
Copper clad laminate (CCL) is the main material used to make printed circuit boards (PCBs). CCL has three main functions: conductivity, insulation, and support. Because of this, they are known as the “mother of electronic products.” The core structure is made of a resin and reinforcing materials base, a conductive copper foil, and an adhesive layer. These are put together through the lamination process, which involves heating and pressurizing the materials.
1. Basic Concepts of Copper Clad Laminate
1.1 Core Definition
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) is the core basic material used in manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs). It’s basically a composite sheet, which is a plate made by soaking a reinforcing material (usually insulating) with a resin binder (insulator) and then hardening it. It’s then pressed into place to cover one or two layers of conductive copper foil on one or both sides.
1.2 Key Components of A CCL
You can think of it as a “sandwich”:
Top/Bottom Layer (optionally single- or double-sided): Thin copper foil (conductor).
Core Layer: Insulated substrate (insulator + reinforcement) that provides strength and rigidity.
①Copper Foil
1) Role: Conductive layer. Through the etching process, to form circuit alignment, pads, large areas of copper (ground layer, power layer), and other conductive graphics.
2) Thickness: Commonly used thicknesses are 1/2 oz (about 18μm), 1 oz (about 35μm), 2 oz (about 70μm), etc. Thinner copper foils are used for fine circuits. Thinner copper foils are used for fine circuits, and thicker ones are used for high currents.
3) Types: Mainly calendered copper foils (good ductility) and electrolytic copper foils (less expensive and commonly used).
② Insulating Substrate / Reinforcing Material
1) Function:
Electrical Insulation: Separates different layers of copper wiring to prevent short circuits.
Mechanical Support: Provides structural strength, rigidity, and dimensional stability of the PCB.
Thermal Conductivity: (part of the material) helps to dissipate the heat generated by the electronic components.
Bonding Medium: Bonds copper foils together securely (for multilayer boards, also used to bond inner core boards).
2) Commonly Used Materials:
FR-4: The absolute mainstream material. Made of epoxy resin impregnated woven glass fiber cloth (E-glass). It has good mechanical strength, electrical insulation, flame retardant (FR-Flame Retardant), and relatively low cost. Suitable for most general-purpose electronic products.
FR-1/FR-2: Paper-based phenolic resin material. It’s cheap, but it doesn’t perform well electrically, and it’s not strong enough to resist heat and humidity. It’s mainly used for single-sided, low-cost consumer electronics (like toys and small appliances).
CEM-1/CEM-3: Composite epoxy substrate. CEM-1 is paper core + fiberglass face, CEM-3 is fiberglass nonwoven core + fiberglass cloth face. The performance is between FR-4 and FR-1, and the cost is also medium, commonly used for single-sided or simple double-sided boards.
High Frequency/High Speed Materials: such as PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), PPO / PPE (polyphenylene ether), ceramic-filled materials. Low dielectric constant, low dielectric loss factor, suitable for high-frequency (e.g., RF, microwave) and high-speed digital circuits (e.g., 5G, high-speed SerDes).
Metal Substrates: such as aluminum substrates (the most common), copper substrates. The insulation layer is below the metal layer. Its main purpose is to provide excellent thermal performance. That is, it acts as a heat sink. It is used for high-power LEDs, power supply modules, and so on.
Flexible Substrates: Some examples of materials used are polyimide and polyester film. It is used to make flexible circuit boards or boards that combine flexibility and rigidity.
③ Resin Adhesive
1) Function: Infiltrate and bond the reinforcing material (e.g., glass fiber cloth) and firmly bond the copper foil to the substrate. The properties of the resin (e.g., Tg – Glass Transition Temperature, CTE – Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, Dielectric Properties, Heat Resistance, Flame Retardant, etc.) largely determine the overall performance of the copper clad laminate (especially heat resistance and electrical properties).
2) Commonly Used Resins: epoxy resin (FR-4), phenolic resin (FR-1/FR-2), polyimide (high-end, flexible), PTFE (high-frequency), BT resin (high-speed), and so on.
thickness and electrical properties are determined by the type of Prepreg used. Common glass styles include:
-
1080: Very thin (approx. 0.06mm), used for high-layer count or thin PCBs.
-
2116: Medium thickness (approx. 0.11mm), offers a balance of cost and stability.
-
7628: Thickest common style (approx. 0.18mm), provides high rigidity and lower cost for standard boards.
-
Flat Glass Cloth: Used in high-speed digital designs to reduce “Fiber Weave Effect” and ensure signal integrity.
2. Main Functions of CCL
Carrying Components: Provide physical mounting platforms (pads, holes) for electronic components.
Forming Electrical Connections: Forming designed circuit leads and connections (pads, vias) through etched copper layers to realize electrical interconnections between components.
Provide Electrical Insulation: The substrate isolates conductors in different layers and areas to prevent short circuits.
Provides Mechanical Support: Gives the PCB overall structural strength and rigidity to support components and withstand the stresses of assembly and use (insertion, removal, vibration, shock).
Heat Dissipation (some types): Helps to conduct and dissipate heat generated by components, especially on metallic substrates or substrate materials with good thermal conductivity.
Signal Transmission Medium: A medium whose dielectric properties directly affect the quality of high-speed signal transmission (signal integrity).
3. Main Types of Copper Clad Boards
1) According to the Number of Layers in the Structure:
Single-sided Board: copper foil on one side only.
Double-sided Board: Both sides have copper foil.
Multi-layer Board: As the inner layer of a multi-layer PCB (core board with etched circuits) or as an adhesive/semi-cured sheet for laminating multi-layers.
2) By Reinforcing Material:
Glass Cloth Base (FR-4, CEM-3 Top Layer, etc.) ;
Paper Base (FR-1/FR-2) ;
Composite Base (CEM-1, CEM-3) ;
Nonwoven Base ;
Special Material Base (Ceramics, Metal, etc.).
3) By Resin Type:
Phenolic Resin (Paper Substrate) ;
Epoxy Resin (FR-4, CEM Series) ;
Polyimide Resin (high-end, Flexible) ;
PTFE Resin (high Frequency) ;
BT Resin (High Speed) ;
etc.
4) By Performance Characteristics:
General Purpose (FR-4) ;
High Tg Type (High Temperature Resistant) ;
Halogen Free Type (Environmentally Friendly) ;
High Frequency and High Speed Type (Low Dk/Df) ;
High Thermal Conductivity Type (Metal Substrate, Thermally Conductive Filled FR-4) ;
High CTI Type (High Leakage Mark Index Resistant) ;
Flexible Substrates.
Choosing the Right Copper Foil for High-Speed Designs Not all copper layers are created equal. Depending on the frequency, you may need:
-
HTE (High Temperature Elongation): Ideal for multilayer boards to prevent cracks during thermal stress.
-
RTF (Reverse Treated Foil): Offers better peel strength while maintaining relatively low profile for signal integrity.
-
VLP (Very Low Profile): Essential for 5G and microwave circuits. It minimizes “Skin Effect” losses by providing an ultra-smooth conductor surface.
| CCL Category | Common Base | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
| Standard Rigid | FR-4 (Epoxy) | Versatility & Low Cost | Consumer Electronics |
| High-Frequency | PTFE / Ceramic | Low Signal Loss (Df) | 5G, Radar, Satellite |
| Thermal/Metal | Aluminum / Copper | High Heat Dissipation | LED Lighting, Power Modules |
| Flexible (FPC) | Polyimide (PI) | Bendable & Lightweight | Smartphones, Wearables |
4. Copper Clad Boards Production Process

1) Resin Adhesive Preparation: Mix resin, curing agent, solvent, filler, flame retardant, etc., according to the formula.
2) Dipping: Reinforcement materials (such as glass cloth) are dipped through the dip tank, impregnated with resin glue.
3) Semi-cured Sheet Preparation: The impregnated material passes through the oven to evaporate the solvent and make the resin partially cured to make a semi-cured sheet.
4) Stacking: Copper foil (single or double-sided) and semi-cured sheet are stacked together according to the design requirements.
5) Pressing into Shape: The material is fed into a hot press. The high temperature and pressure make the resin fully dry, stick the copper foil and partially dry sheet together, and form a hard, flat sheet.
6) Post-processing: Cutting, grinding, inspection (thickness, size, appearance, electrical properties, heat resistance, etc.).
5. Copper Clad Laminate Application Areas
Copper clad laminate technology is improving. It is becoming better at conducting heat, working at high speeds, and being flexible. This supports new uses for electronic devices in communication, computing, mobile devices, and other new fields.
1) Communication Equipment
5G base station antennas, microwave components, satellite communication systems, military radar, and other high-frequency communication scenarios.
High-performance signal transmission support for servers, data center infrastructure, and artificial intelligence hardware.
2) Computers & Smart Terminals
Circuit integration for computer motherboards, servers, consumer electronics (cell phones/tablets), and wearable devices.
High Density Interconnect (HDI) technology makes devices smaller. For example, it is used in the multi-layer PCB design for smartphones.
3) Automotive Electronics
In-vehicle control systems, sensors, lighting modules, and power management for new energy vehicles.
Heat- and moisture-resistant materials are needed to ensure stability in harsh environments.
4) Consumer Electronics and Home Appliances
White goods, smart home controllers, and LED lighting driver circuits.
5) Frontier Technology
High-speed signal processing modules for humanoid robots and AI hardware;
High-reliability circuit boards for aerospace equipment and medical implants.
6. How to Choose the Right Copper Clad Laminate for PCBs?
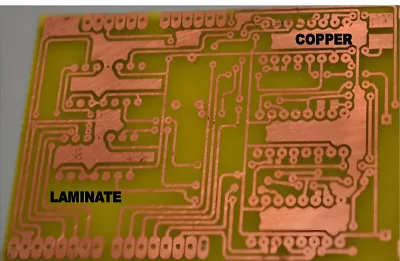
To choose the right CCLs, you need to consider their electrical and physical properties, as well as how and where they will be used. The following are the most important things to think about:
6.1 Core Performance Parameters
1) Electrical Performance Priority Indicators
Dielectric Constant (Dk): For high-frequency scenarios (e.g., 5G base stations, AI servers), boards with Dk ≤ 3.5 should be selected to reduce signal delay and crosstalk.
Dielectric Loss Factor (Df): To reduce signal loss during high-speed transmission, the Df value needs to be less than 0.02. The lower the Df value, the better the signal integrity.
2) Physical Reliability Parameters
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): ordinary FR-4 plate Tg is 130~140℃, high temperature environment needs to use modified resin plate with Tg increased to 160~200℃, but the cost increases accordingly. The cost will increase accordingly.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) & Dimensional Stability: CTE needs to match how the components change shape when heated. The size should be controlled within ±0.1 mm. Large-sized PCBs need to be made stronger by changing the resin.
6.2 Application Scenario Customized Selection
| Application Areas | Core Requirements | Recommended Sheet Types |
| Communication Equipment | High-frequency Signal Low-loss Transmission | Modified PTFE Substrate (low Dk/Df) |
| AI Servers | High-speed Data Processing and Heat Dissipation | Acenaphthene Olefin Resin Substrate (very low loss) |
| Automotive Electronics | High-temperature-resistant, high-reliability | Metal Substrate/Thick Copper Plate ( ≥3oz) |
| Consumer Electronics | Thin and Lightweight, High-density Wiring | HDI Substrates/Flexible Copper Clad Laminates |
6.3 Suggestions for Selection Practices
Balance of Cost and Performance: FR-4 is optional for regular scenarios; high-frequency and high-speed scenarios require acceptance of high-cost materials (e.g., modified resin boards).
Verification of Certification Standards: Boards that meet certain standards are given priority. These standards include IPC-A-600 (size and appearance), UL94 (flame retardant), and RoHS (environmental protection).
Process Compatibility: surface copper foil flatness needs to be ≥ 95% (HASL process), to avoid chemical solvent corrosion due to insulation degradation during etching.
When choosing a CCL for your project, verify these critical specifications:
-
Tg (Glass Transition Temperature): For lead-free soldering, a High-Tg (≥170°C) material is mandatory to avoid delamination.
-
Dk & Df (Dielectric Constant & Loss): For RF or high-speed digital circuits, select low Dk/Df materials (like PTFE) to minimize signal attenuation.
-
CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion): Ensure the CTE matches your components to prevent solder joint fatigue.
-
UL 94V-0 Rating: Confirm the flame retardancy for safety compliance.
7. CCL FAQs
CCL (Copper Clad Laminate), also called Copper Clad Substrate in Chinese, is made of copper foil pressed with an insulating material like resin or fiberglass. It’s a key raw material for PCBs.
CCL is the main material used to make PCBs. PCBs are made in factories that process CCL. To make a PCB circuit board, CCL must go through a long and complicated process with many steps, such as drilling, plating, and etching.
CCL can be divided into two types, symmetric and asymmetric, based on how the copper foil is arranged. Flexible copper-clad laminate (FCCL) is divided into two types. The first type has three layers (copper foil-film-adhesive). The second type has two layers (insulating base film-metal foil). The first type is used for bulk soft boards. The second type is used for high-level soft and hard composite boards.
CCL is formed into lines by removing unwanted copper foils through a process called “photochemical etching”. Then, it is processed into finished PCBs through drilling, plating, and soldering. Rigid boards usually use a type of resin called FR4, while flexible circuit boards (FPC) use a type of film called polyimide.
The material expands and contracts a lot with temperature changes. The way copper clad laminates for circuit boards change size when heated up or cooled off is different from other materials. This can make the circuit boards bend or crack when the temperature changes.
The copper layer acts as a conduction path for electrical signals, while the substrate provides mechanical support and insulation. The quality and characteristics of the copper cladding significantly affect the performance of the PCB, and therefore the performance of the electronic devices that use it.
8. Summary
PCBs are the cornerstone of modern electronic devices. It is not only a physical carrier, but also a core platform for key functions such as electrical connection, signal transmission, component support, and heat dissipation. Without copper clad laminates, there would be no printed circuit boards (PCBs), and there would be no electronic products we use in our daily lives. Understanding the composition of a copper clad laminate (copper conductor + insulating substrate) and the characteristics of different types of materials (e.g., FR-4 versatility, low loss of high-frequency materials, heat dissipation of metal substrates) is the basis for PCB design, material selection, and manufacturing.
Get Your PCB Quote!